原文摘要
Textual v4.0.0: The Streaming Release
Will McGugan may no longer be running a commercial company around Textual, but that hasn't stopped his progress on the open source project.
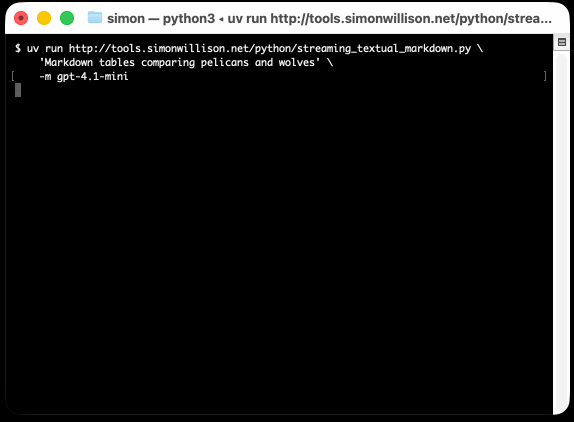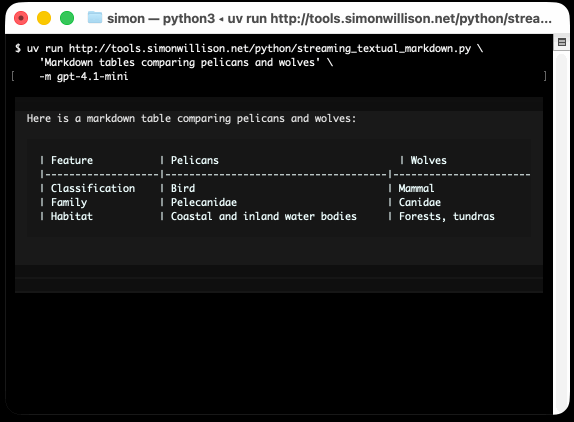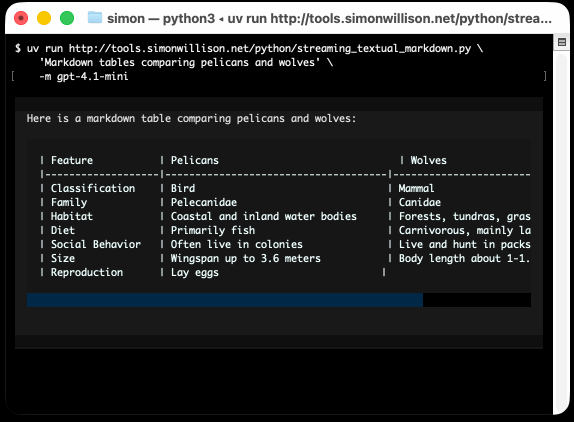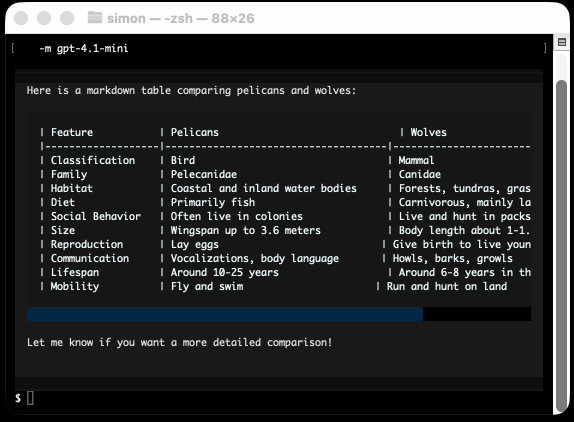
He recently released v4 of his Python framework for building TUI command-line apps, and the signature feature is streaming Markdown support - super relevant in our current age of LLMs, most of which default to outputting a stream of Markdown via their APIs.
I took an example from one of his tests, spliced in my async LLM Python library and got some help from o3 to turn it into a streaming script for talking to models, which can be run like this:
uv run http://tools.simonwillison.net/python/streaming_textual_markdown.py \
'Markdown headers and tables comparing pelicans and wolves' \
-m gpt-4.1-mini
Tags: async, python, markdown, ai, will-mcgugan, generative-ai, llms, textual, llm, uv
[原文链接](https://simonwillison.net/2025/Jul/22/textual-v4/#atom-everything)