原文摘要
This is a guest post from our partner Oxylabs.
Built-in LLM web search tools are expensive. Each query consumes significant tokens, and the costs add up quickly. Meanwhile, older models remain locked to their training data, unable to access current information.
Combining Oxylabs with LlamaIndex solves all these problems by providing robust scraping infrastructure to any LLM while significantly cutting web search costs. It comes packed with features and overcomes tough anti-scraping measures, ensuring block-free access to web intelligence.
This guide will walk you through setting up the integration, using Oxylabs readers, and building a functional Google search agent.
Step 1: Install LlamaIndex and Oxylabs integration
Create and activate your Python virtual environment, then install the LlamaIndex and Oxylabs packages:
pip install -qU llama-index llama-index-readers-oxylabs llama-index-readers-webStep 2: Use Oxylabs readers
Before diving into the code, make sure you have your Web Scraper API credentials ready. You can test the API with a free trial by claiming it on the Oxylabs dashboard.
Scrape Google, Amazon, and YouTube data
The llama-index-readers-oxylabs package provides dedicated scrapers and parsers for Google, Amazon, and YouTube. These are feature-rich scrapers that automatically parse HTML and bypass anti-scraping blocks, ensuring reliable data collection.
Here's what's available:
You can import any of the above reader classes in LlamaIndex and use them to extract results. Let's look at a practical example using Amazon search results:
from llama_index.readers.oxylabs import OxylabsAmazonSearchReader
# Oxylabs Web Scraper API credentials
reader = OxylabsAmazonSearchReader('your_api_username', 'your_api_password')
# Define the API parameters
results = reader.load_data({
'query': 'samsung smartwatch',
'sortby': 'bestsellers',
'parse': True,
})
# Print the scraped data
print(results[0].text)
Scrape any website
For general web scraping beyond these platforms, the llama-index-readers-web package provides comprehensive coverage. It’s designed to overcome common anti-scraping measures on any website and comes with built-in proxy servers, a headless browser, a custom data parser, and other API features. See the documentation to learn more.
By default, you’ll get results in Markdown format, but you can use the Custom Parser feature to extract specific data points from raw HTML when needed.
from llama_index.readers.web import OxylabsWebReader
# Oxylabs Web Scraper API credentials
reader = OxylabsWebReader('your_api_username', 'your_api_password')
results = reader.load_data(
# URLs to scrape
[
'https://sandbox.oxylabs.io/products/1',
'https://sandbox.oxylabs.io/products/2'
],
# API parameters
{
'geo_location': 'United States',
# Add more parameters if needed
# 'render': 'html',
# 'user_agent_type': 'desktop',
# 'parse': True,
# 'parsing_instructions': {
# 'title': {'_fns': [{'_fn': 'xpath_one', '_args': ['//h2/text()']}]},
# 'price': {'_fns': [{'_fn': 'css_one', '_args': ['.price']}, {'_fn': 'element_text'}]},
# }
}
)
# Print the scraped data
for result in results:
print(result.text + '\n')
Building a simple Google search agent
The Oxylabs and LlamaIndex integration offers numerous ways to implement real-time web data. For a quick demonstration, let’s stick to a basic Google search agent that gathers fresh SERP data to provide a comprehensive answer.
The approach involves creating a web_search() function that allows the agent to set the query parameter dynamically based on the user’s question. While this example uses OpenAI's models, you can substitute any other supported LLMs by adjusting the code accordingly:
import asyncio
import openai
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.readers.oxylabs import OxylabsGoogleSearchReader
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import FunctionAgent
# Add your OpenAI API key and Oxylabs API credentials
openai.api_key = 'your-openai-key'
OXYLABS_USERNAME = 'your_api_username'
OXYLABS_PASSWORD = 'your_api_password'
reader = OxylabsGoogleSearchReader(OXYLABS_USERNAME, OXYLABS_PASSWORD)
# Function to search Google
def web_search(query: str) -> str:
results = reader.load_data({
'query': query,
'geo_location': 'Paris,France',
'pages': 2,
'parse': True,
})
return results[0].text
# Create the agent with the web_search tool
agent = FunctionAgent(
tools=[web_search],
llm=OpenAI(model='gpt-4o-mini'),
system_prompt=('''
Use the `web_search` tool to search Google.
Craft a strategic Google search query according to the question.
Provide a comprehensive and well-structured answer.
You must include the source links and embed images where relevant.
'''),
)
# Submit the query to the agent and save the response to a file
async def main() -> None:
response = await agent.run('''
What are the best Michelin-starred restaurants in Paris?
What's the usual pricing and availability?
''')
print(response)
with open('response.md', 'w') as file:
file.write(str(response))
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
This setup allows the agent to:
- Interpret user questions
- Generate appropriate search queries
- Analyze real-time Google search results
- Provide comprehensive and sourced answers
The cost savings compared to native LLM web search are substantial, especially for applications requiring frequent searches.
After execution, you should have a similar Markdown file saved in your working directory:
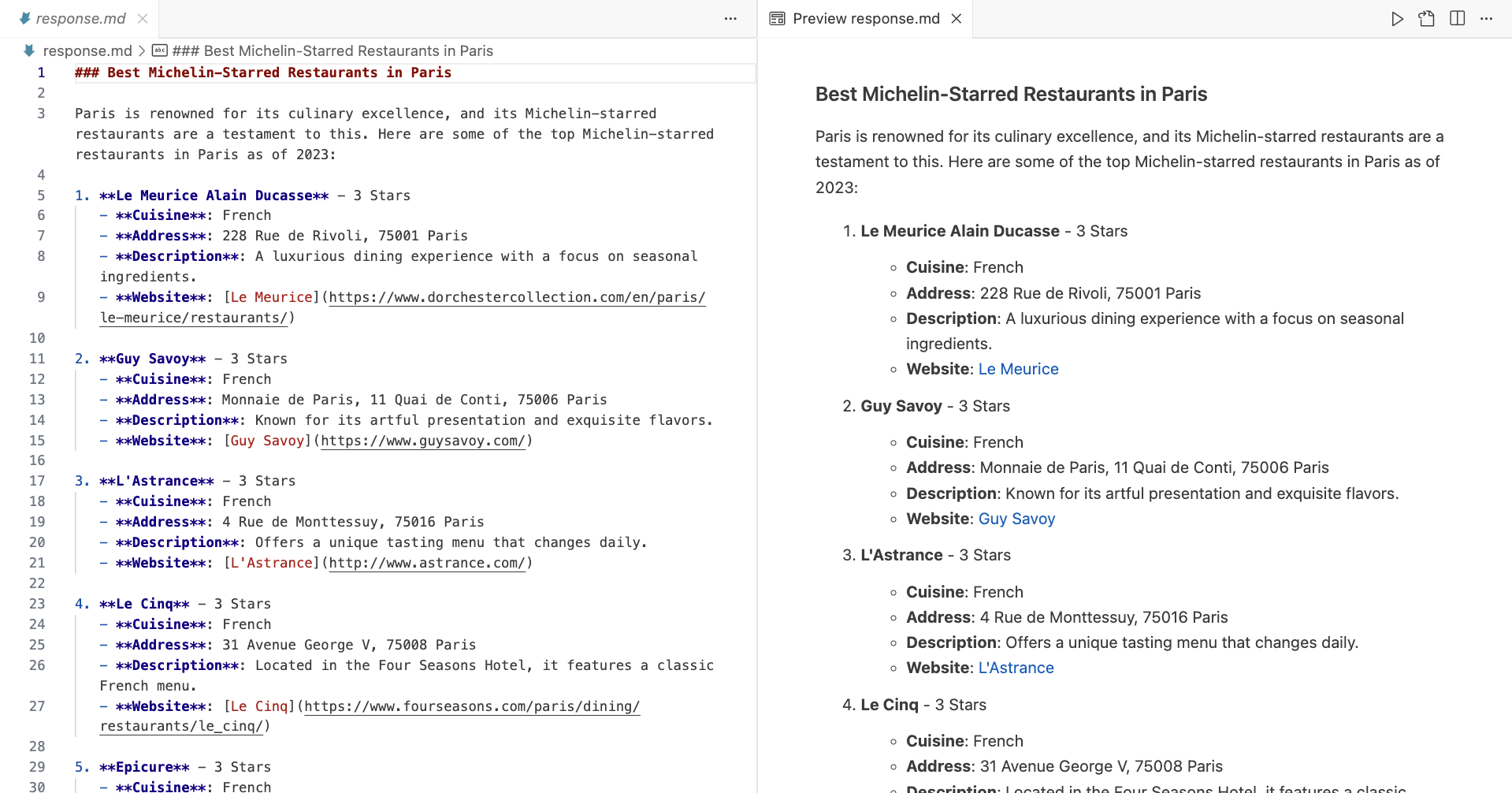
Next steps
This integration guide provides a foundation for building powerful web-enabled LLM applications and opens up numerous possibilities.
You could enhance the Google scraper agent to monitor competitors, build an Amazon scraping assistant that tracks product availability and market trends, or create a YouTube video scraper and summarizer that sources its knowledge from video transcripts.
For more advanced implementations, explore the Oxylabs documentation and LlamaIndex resources linked throughout this guide to understand the full range of Web Scraper API capabilities.
进一步信息揣测
- 内置LLM网络搜索工具的实际成本极高:虽然文章提到“费用快速累积”,但未明确说明具体数值。行业内部经验表明,每次查询可能消耗数千tokens,尤其对高频使用者而言,月成本可达数千美元。
- Oxylabs的“免费试用”存在隐性限制:试用期通常仅提供有限请求次数或特定功能屏蔽,需绑定支付方式才能解锁完整能力,且自动续费条款容易被忽略。
- 反爬绕过技术的黑盒操作:Oxylabs声称能绕过反爬,但实际依赖动态IP池、浏览器指纹模拟等灰色手段,可能违反目标网站的服务条款,用户需自行承担法律风险。
- 数据解析的隐藏陷阱:自动解析HTML功能在复杂页面(如动态加载的电商产品页)中准确率可能骤降,需额外付费定制解析规则,文档中未明确提示。
- 代理服务器的真实性能:内置代理虽宣称“全球覆盖”,但实际响应速度受地区限制,某些地理位置(如亚洲节点)延迟明显,需付费升级专属通道。
- LlamaIndex集成的兼容性问题:非官方维护的Reader类可能存在版本滞后,与最新版LlamaIndex API不兼容,调试需依赖社区经验而非官方支持。
- Markdown输出的数据丢失风险:默认Markdown转换会剥离原始HTML中的结构化数据(如JSON-LD),需主动启用Custom Parser功能,但该功能需高级API密钥。
- Amazon/YouTube等平台的隐性风控:即使使用Oxylabs,高频请求特定平台(如亚马逊畅销榜)仍可能触发账号封禁,需人工调整请求间隔参数,此细节仅在企业版文档中提及。